When it comes to engineering and design, the introduction of Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) has been nothing short of a revolution. But what exactly is CAE?
Introduction to Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE)
At its core, CAE is a broad term used to describe the use of computer software to help engineers with design and testing. It includes simulation, design checking, and improving products or assets before they’re made and constructed.
Originally, CAE was mostly used in aerospace and car manufacturing. But now, it’s in many industries to help designs become more accurate, faster, and more creative. With CAE, engineers can test ideas and solve problems before building physical models.
Studies show that integrating CAE tools can enhance product quality, and reduce development time and costs. This speeds up the time it takes for products and assets to reach the market, but also fosters a creative environment where engineers are free to explore solutions to a variety of problems and challenges.
In this post, we will explore the various aspects of CAE and how it has revolutionized the engineering industry. We’ll discuss its benefits, applications, and future prospects.

Photo by ThisisEngineering on Unsplash
Understanding the Core Components of Computer-Aided Engineering
Understanding the pillars that form the foundation of Computer-Aided Engineering enables us to push the boundaries of what’s possible in product design as well as complex infrastructure design. Let’s look at CAE through the lens of wastewater treatment plant & electrical substation design—time-intensive processes that involve multiple engineering disciplines.
Simulation
Computer simulations are the heart of CAE, breathing life into our design concepts even before they materialize. It’s the process of using computer software to model the behavior of a product under various conditions to test how it works.
Imagine constructing a bridge or designing a new car but you can test its durability and performance in a virtual environment, first. This tool can be used similarly during wastewater treatment plant and electrical substation design—engineers are able to test designs and layouts before actually building prototypes.
According to a study by the Master of Science Thesis journal, simulation can reduce physical prototype testing, significantly slashing both the time and cost of the product development process. Engineering simulation empowers engineers to identify potential issues and correct them early in the design phase, making it a valuable tool in the engineering toolbox.
Analysis
Analysis involves a detailed examination of every aspect of the proposed design. From analyzing the load-bearing capacity of a structure to assessing the heat dissipation in a transformer, analysis aids in testing not only the functionality but also the efficiency of substations.
This is especially important during the substation design process as it helps give the design better performance and reliability. In addition to improving the lifetime quality of the asset, this also helps identify flaws early.
Optimization
Finally, we have optimization, the process of making something as effective as possible. In the context of CAE, it’s about fine tuning our designs to achieve the best performance, cost-efficiency, and sustainability.
Whether it’s enhancing the efficiency of wastewater treatment processes or selecting the most cost-effective equipment materials, optimization ensures that we’re not only creating functional products but also ones that are tailored for real-world wastewater management.
How Computer-Aided Engineering Works
Now that we’ve dived into the core components of computer-aided engineering (CAE), it’s time to peel back the curtain and reveal the magic behind the scenes. How does CAE transform a spark of an idea into a tangible, optimized product ready for the real world?
Modeling in a Virtual Environment
At the soul of CAE is the ability to model designs in a virtual environment, a process that fundamentally changes the game for engineers and designers alike. It involves constructing a dynamic, interactive model that behaves just as it would in the real world. A study by Texas A&M University and Stanford University found that virtual modeling can improve the quality of initial design concepts.
This dramatic jump in precision early in the design phase can have cascading positive effects on the entire development lifecycle, ensuring that subsequent stages of simulation, analysis, and optimization are built on a solid foundation.
Integration with Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Integration with computer-aided design (CAD) systems is where the synergy comes into play, bridging the gap between conceptual design and engineering analysis. CAD provides detailed schematics and drawings, while CAE leverages these designs to simulate and analyze their performance.
This seamless integration not only streamlines the development process but also fosters a more collaborative environment where adjustments can be made on the fly, ensuring that the final product is optimized for efficiency and innovation.
Advantages of Implementing Computer-Aided Engineering
After exploring the magic behind CAE, you might be wondering, “What does this mean for me and my project?” Well, these benefits of implementing CAE tools are high not just for individual engineers but for the entire engineering process and project lifecycle.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
First, CAE is a powerhouse when it comes to cost reduction and efficiency. Imagine being able to predict and solve problems before a single prototype is even built.
CAE can reduce prototype costs because it allows for detailed analysis and simulation, so errors can be caught and corrected in the virtual world, saving a fortune on physical testing and iterations. It can help trim expenses AND optimize project resources.
Accelerated Product Development
In today’s fast-paced market, speed is everything. CAE equips teams with the tools to move from concept to completed project at an unprecedented pace. For instance, generative design software such as the Transcend Design Generator expedited the process of selecting optimal substation locations for a major power utility’s community solar projects.
By running multiple conceptual designs and generating detailed documentation, TDG enabled quick decision-making, leading to faster bids, reduced risk of scope changes, and streamlined vendor evaluation.
This breakthrough platform not only shaved weeks off the project timeline but also infused the entire process with a level of precision and foresight that was previously not reachable.
Improved Performance and Reliability
The dynamic simulation and analysis capabilities of CAE result in products & assets that are engineered to boost peak performance and reliability. This boost is largely attributed to the comprehensive view that CAE provides, allowing engineers to anticipate and counteract potential fail points before they become an issue.
Emerging Trends in Computer-Aided Engineering
There is much to celebrate about CAE and the implications it has on modern manufacturing and technology. Several emerging trends have already begun to catch on throughout industries around the world.
AI and Machine Learning (ML) Integration
While traditional CAE methods have been effective, they often involve extensive intervention in the form of many design iterations and various levels of troubleshooting.
This can lead to increased costs and longer development phases. However, with AI and ML becoming integrated into the process, everything can be simplified, streamlined, and more effective.
Cloud-Based CAE Solutions
With cloud-based CAE solutions, engineers will be able to work more efficiently, with their processes, simulations, and methods all streamlined on a cloud. When everything is kept in one place, the need for multiple rounds of testing disappears, and engineers are free to boost productivity and overall design quality.
Real-Time Simulation
Real-time simulation involves using models on a computer to simulate physical systems and processes—all in real time. This means the simulation is able to run at the same speed as actual time, so engineers can interact with the system manually. Testing and optimization of designs and systems can be done in the simulator, before physical prototypes or complete assets are built, saving time, money, and manpower.
Exploring Generative Design Software
Like CAE, generative design software is akin to having a supercomputer brainstorm alongside you, pushing the boundaries of creativity and efficiency. It uses algorithms and artificial intelligence to generate a plethora of design options based on specific parameters and constraints you feed it. Think of it as evolution on fast-forward, finding the fittest design solutions that exceed your project’s criteria.
Role of Transcend Design Generator in Transforming Designs
Enter the Transcend Design Generator (TDG), the leading generative design software for critical infrastructure. This powerful platform is revolutionizing the way we approach design in both the power and water industries, by streamlining and enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of preliminary design processes.
For the Power Industry
TDG offers a significant advantage in designing substations and power delivery systems. It’s simple, yet powerful, user interface means that even non-experts can input initial parameters, and the system handles the rest.
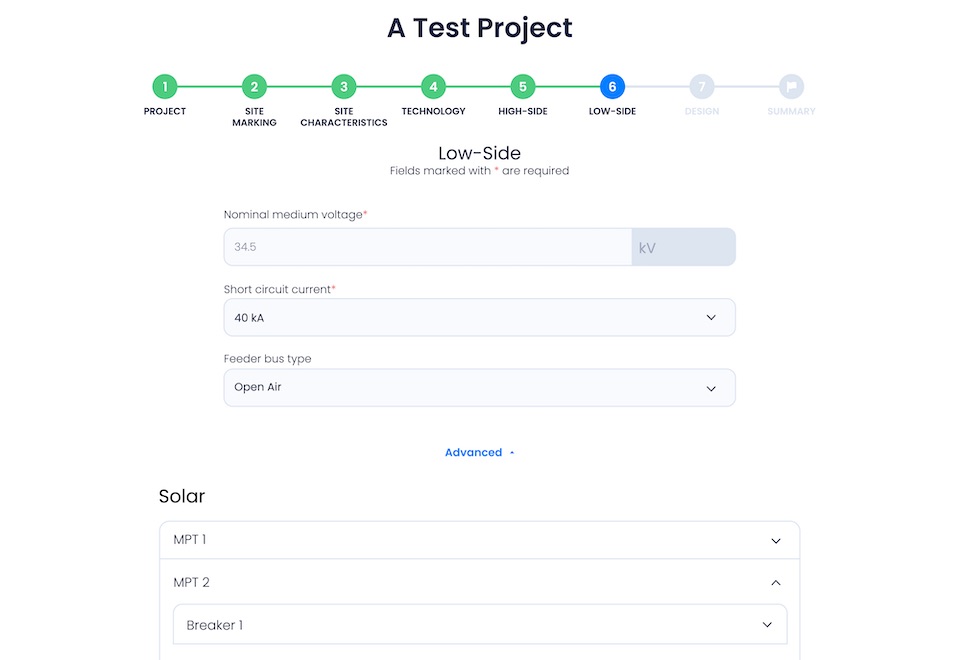
This collaborative method of design allows for broader innovation within teams. The integration of specific data validation and the ability to incorporate custom parameters means designs can be rapidly optimized to meet the unique demands of power infrastructure projects.
The result? Faster project timelines and the potential to significantly reduce development costs while still achieving high-performance outcomes.
For the Water Industry
In the water sector, TDG shines by making the complex process of wastewater treatment facility design both accessible and highly efficient. Users from a spectrum of expertise levels, from novices to seasoned engineers, can leverage TDG’s intuitive interface to input key design parameters.
The system’s automated process design simulation takes over, utilizing data from proprietary databases and running through industry-standard treatment simulators. This results in highly detailed process schemes and documentation, paving the way for precise equipment selection and ultimately, the generation of sophisticated Building Information Modeling (BIM).
By enabling easy adjustments and ensuring the accuracy of every element of the design, TDG significantly reduces the risk of costly revisions and accelerates the move from concept to completion.
Final Thoughts
It’s clear that CAE and generative design software are innovative in the truest sense. Whether you’re in the power industry or navigating the intricate waters of the water sector, TDG is poised to transform your projects from good to spectacular, efficiently and reliably. Imagine slashing your project timelines, cutting down costs, and pushing the envelope of design innovation—all with a few clicks. That’s the power of TDG.
Ready to revolutionize your design process and outcomes? Explore how partnering with TDG can elevate your next project to unparalleled heights.
FAQs
What is the difference between FEA and CAE?
FEA stands for Finite Element Analysis, and is a specific method within CAE that is primarily used for structural analysis of solids and structures, such as stress and formation while under a heavy load.
What is the difference between CAD and CAE?
While both are computer-aided technologies used in engineering, CAD specifically stands for computer-aided design, and serves a different purpose than CAE. CAD is meant to create and modify 2D or 3D models of products, while CAE simulates and analyzes the behavior of the designs.








 WWTP Design
WWTP Design  Substation Design
Substation Design  Utility Interconnection Hub
Utility Interconnection Hub  White Label Proposal Generator
White Label Proposal Generator  PFAS Feasibility Study
PFAS Feasibility Study  Booster Station Design
Booster Station Design  Value Discovery Program
Value Discovery Program